User Interface (UI) as well as User Experience (UX) design are the two most critical disciplines that focus solely on the development of usable, accessible, and enjoyable digital products. The main focus of UX is the overall user feeling as well as the ease of interaction with the product.
UI is the part that deals with visuals. Hence, it is responsible for things like layout, colour, and typography. In brief, UI/UX experts ensure that digital tools are user-friendly, solve users’ problems, and achieve the set business goals. The main point of using such a strategy is to be able to keep very high customer retention and achieve solid conversion rates that are really effective.
The Fundamental Principles of User Experience (UX)
UX design is mainly based on empathy, research, and it also undergoes a lot of testing during each stage of the product development lifecycle. The main objective is to help the user solve the problems he/she have and at the same time to try to eliminate the occasions of user-product interaction.
Effectively doing UX means having a very thorough understanding of user motivations, surroundings, and issues. The designer uses such techniques as user interviews, persona creation, and journey mapping to get insights for their strategic decision-making. Proper UX makes sure that the logic behind the product’s scaffolding, as well as the flow of it, remains stable, and it is easy for users to navigate through it all the time.
The process of UX design begins with an empathetic understanding of a particular community. Relying mostly on user research, it unearths the essential needs and behaviours. Information architecture is the tool that keeps content structured for better understanding and easier access. To verify if the product is easy to use, testing is done, and the goal is to find interaction issues that can be solved quickly.
User flows and journey maps serve as a visual representation of the entire customer journey in an efficient manner. Efficiency and satisfaction of the users are the primary metrics of the success of this method. To further know about it, one can visit UI UX Online Training.
Defining and Executing User Interface (UI) Design
Through UI, the company gets to showcase the distinctiveness of the product in an artful and catchy way. Among the most straightforward elements that a person sees in an application, such as buttons, signs, and menus, the visual presentation is included. To accomplish this, UI designers concentrate on visual coherence, brand identification, and visual organisational techniques that lead the user’s eye correctly.
Designing in accordance with design systems and accessibility standards is the main factor in completing a professional interface. The friendliness of the UI positively affects the view of the product’s general quality, and hence it is something very essential. Many institutes provide UI UX course in Noida, and they can help you get a high-paying job in this domain.
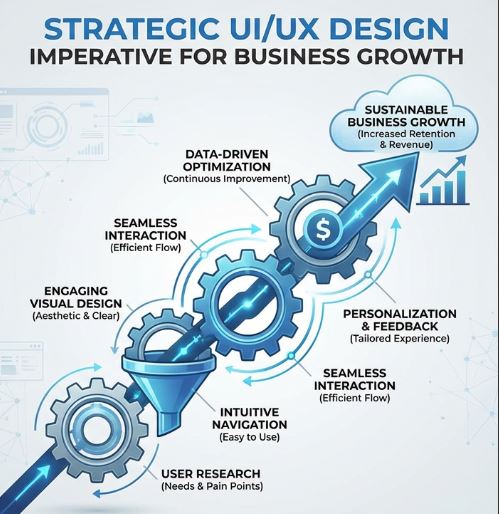
The chief function of UI is to set up the visual hierarchy so as to steer user attention in the right place. Brand identity is very effectively conveyed through the use of colour palettes, typography, and imagery. There is a strict enforcement of consistency in design patterns and component libraries.
Moreover, UI has to make sure that users with disabilities have easy access to all elements. Designers work out their developer handoff in detailed high-fidelity mockups. The result should be a gorgeous yet user-friendly interface that appears time and again without fail.
The Power of Prototyping and Collaborative Tools
Present-day UI/UX workflow cannot do without the fantastic digital prototyping as well as the collaboration tools that have greatly facilitated the work of designers and team members in different locations. Figma is undoubtedly one of the most advanced and versatile applications of our time on the market, and it is regarded as a standard tool in the industry.
Teams can work on the project files quickly and effortlessly since, with the help of these tools, the loss of very expensive development time can be prevented by testing the ideas to be put forward. Prototyping is done to see the product before it’s done, and thus, it becomes easier to get comments quicker from both the stakeholders and users. This, in turn, helps a team that practices an agile development methodology to adjust rapidly and perfectly meet the customers’ needs.
Figma is an incredible resource for cooperative designing and interactive prototyping. Also, it is a facility that limits no one, as all the designers can instantly work on the same file and offer their input. The use of prototyping tools in a project makes it easy to convey the content of very complicated micro-interactions and animations through visuals.
Wireframing is the beginning step, giving the most attention to the structure and the functionality. Enrolling in the Figma Online Course can help you start a promising career in this domain. High-fidelity prototypes closely replicate the user experience with the final product. Prompt iterations deriving from the input received helped preserve a good deal of resources and time meant for the development period.
Integration of Design Thinking and Agile Methods
UI/UX work closely adheres to the principles of Design Thinking and Agile processes. Design Thinking fosters innovative problem-solving that is based on human needs and quick testing. Agile methods specify designers working in short sprints.
Thus, they can continuously deliver small, testable pieces of functionality in a short time frame. Such a merge design is not seen as a separate phase but rather the ongoing, iterative process that is at the core of the product development cycle. The designer thus becomes a constant strategic partner in the project’s evolution.
Design Thinking operates through the stages of empathise, define, ideate, prototype, and test. Designers, alongside the developers and product managers, work in short sprints. Agile methods focus on the aspects of continuous feedback and easy adaptation.
Design artefacts are produced as minimum viable products (MVPs) for testing. The procedure necessitates unbroken as well as very close contact among all the teams. UI/UX guarantees that each and every new function corresponds with the essential user needs and objectives.
Measuring Success Through Key Metrics
The results of UI/UX activities should be evident and presented through concrete performance indicators. One of the regular metrics is the Task Completion Rate, which is a measure of how many users are able to finish a crucial task quickly.
Time on Task is a gauge of the workflow and the speed of interaction. High Conversion Rates accompanied by low Bounce Rates are clear signs of a good user experience. The designers, by constantly monitoring these quantitative indicators, will therefore be able to accurately present the return on investment (ROI) of their work.
Task Completion Rate is possibly the most important gauge of product usability and success. Time on Task is a measurement of the user’s efficiency in getting through common actions. The Bounce Rate indicates the percentage of single-page sessions that happen in a short period.
Conversion Rates, in turn, are the tools that reveal to what extent business goals have been achieved through the design. System Usability Scale (SUS) is a subjective tool that reflects the user satisfaction level. These are the metrics that create a clear and direct link between quality design and tangible business results.
Conclusion
UI/UX design is a decisive function that combines visual attractiveness with the innate human psychology to come up with effective digital solutions. By basing design decisions on user research and making use of sophisticated tools like Figma, professionals guarantee that their products are not only attractive but also very user-friendly.
To further know about it, one can visit the Ui Ux Certification Course. This particular field, when properly integrated into agile frameworks, is a direct way to better user retention, higher conversion rates, and overall improved brand perception. Hence, putting money into good UI/UX is not really a matter of choice but rather a necessary strategic move for enduring success in the digital world.
